
Understanding Export: A Comprehensive Guide
Exporting is a critical component of global trade, serving as a bridge between producers and consumers across different countries. It is the process through which goods and services are sold to buyers outside the country of origin. For businesses and economies alike, exporting is a key driver of growth, innovation, and international cooperation. This guide will delve into what exporting is, why it matters, and the basic steps involved in the export process.
What is Exporting?
Exporting refers to the act of sending goods or services produced in one country to another for sale or trade. This can involve anything from physical products like machinery, textiles, and food to intangible services such as IT support, consulting, or design. The essence of exporting is to reach markets beyond ational borders, allowing businesses to expand their customer base and diversify their revenue streams.

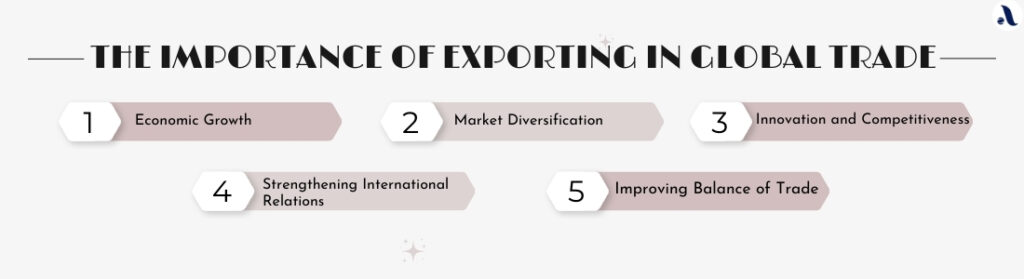
The Importance of Exporting in Global Trade:
- Economic Growth: Exporting is a significant contributor to a nation’s GDP. It
provides businesses with opportunities to scale up production, increases national income, and creates jobs. For many countries, exports are a major source of revenue that drives economic growth and development. - Market Diversification: By exporting, businesses are not limited to their domestic markets. They can tap into international markets, reducing their reliance on local demand and mitigating risks associated with economic downturns in their home country.
- Innovation and Competitiveness: Engaging in international trade exposes businesses to global competition, which can drive innovation and improvements in product quality. This competitive environment encourages companies to adopt best practices, improve efficiency, and develop new products.
- Strengthening International Relations: Exporting goods and services fosters stronger ties between nations. It promotes cultural exchange, economic cooperation, and mutual dependency, contributing to more stable international relations.
- Improving Balance of Trade: A healthy export sector helps improve a country’s balance of trade, which is the difference between its exports and imports. A positive balance, where exports exceed imports, strengthens the national economy and stabilizes the currency.
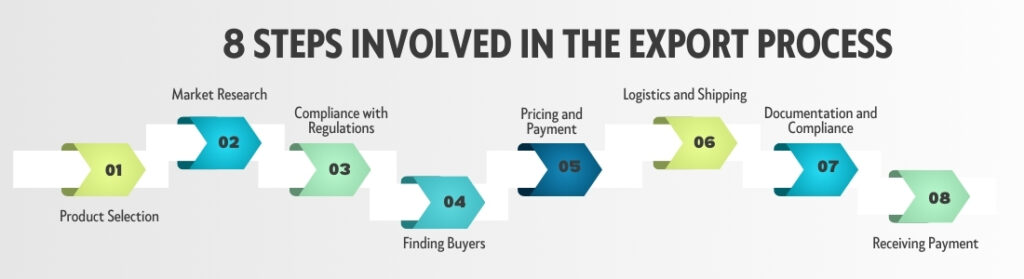
Basic Steps Involved in the Export Process:
- Product Selection: The first step in exporting is selecting the right product or service to export. This involves understanding what products have demand in foreign markets and ensuring that they meet the quality standards required for
international trade. - Market Research: Identifying the right market is crucial. This involves researching potential markets to understand consumer preferences, cultural differences, demand, and competition. Effective market research helps businesses tailor their products to meet the needs of foreign buyers.
- Compliance with Regulations: Exporting requires adherence to international trade laws and regulations. This includes obtaining necessary export licenses, ensuring compliance with both the exporting and importing countries’ regulations, and understanding the legal requirements for shipping goods abroad.
- Finding Buyers: Once the market is identified, the next step is finding buyers. This can be done through trade shows, online marketplaces, or by working with trade agents and distributors who have local market knowledge.
- Pricing and Payment: Setting the right price for exported goods is essential . Exporters need to consider production costs, tariffs, shipping, and other expenses. Additionally, they must establish secure payment terms and methods to minimize financial risks.
- Logistics and Shipping: Efficient logistics are key to successful exporting. This involves choosing reliable transportation methods, understanding customs procedures, and ensuring that goods are packed, labeled, and shipped according
to international standards. - Documentation and Compliance: Exporting requires various documents such as invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and shipping documents. Proper documentation is crucial to ensure smooth customs clearance and to avoid delays.
- Receiving Payment: Once the goods are delivered, the exporter needs to ensure that payment is received according to the agreed terms. This often involves working with banks or payment processing services to handle international transactions securely.
Conclusion:
Understanding the export process is vital for any business looking to expand its reach beyond domestic borders. Exporting not only opens up new markets and revenue streams but also fosters innovation and strengthens international relationships. By following the steps outlined in this guide, businesses can navigate the complexities of exporting and position themselves for success in the global marketplace. Whether you’re a small business or a large corporation, exporting offers vast opportunities for growth and development.
